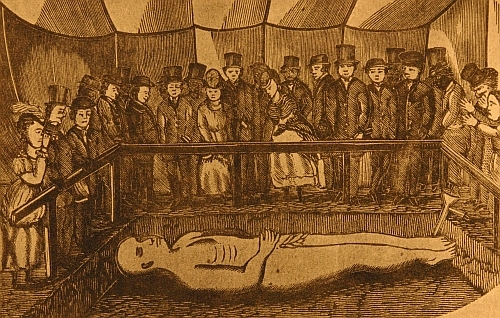
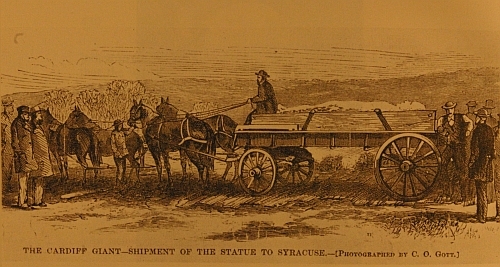
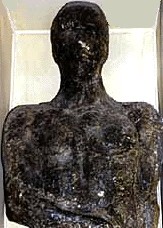
alias: BIG FRANK
BANK BURGLAR
Welcome to the latest Link Dump!Our host for this week stole a pig, and away did run!Reptiles are smarter than you might think.The many lives of Anne Frank.Scientists may have found Noah's Ark. Or maybe not. We shall see.Solving the mystery of a missing mountain climber.The Easter Bunny's controversial history.1891 sea combat in the Pacific.Science has found a way for humans to
More...
Strange Company - 4/18/2025
Included in yesterday’s trip to Fall River was a stop at Miss Lizzie’s Coffee shop and a visit to the cellar to see the scene of the tragic demise of the second Mrs. Lawdwick Borden and two of the three little children in 1848. I have been writing about this sad tale since 2010 and had made a previous trip to the cellar some years ago but was unable to get to the spot where the incident occured to get a clear photograph. The tale of Eliza Borden is a very sad, but not uncommon story of post partum depression with a heartrending end. You feel this as you stand in the dark space behind the chimney where Eliza ended her life with a straight razor after dropping 6 month old Holder and his 3 year old sister Eliza Ann into the cellar cistern. Over the years I have found other similar cases, often involving wells and cisterns, and drownings of children followed by suicides of the mothers. These photos show the chimney, cistern pipe, back wall, dirt and brick floor, original floorboards forming the cellar ceiling and what appears to be an original door. To be in the place where this happened is a sobering experience. My thanks to Joe Pereira for allowing us to see and record the place where this sad occurrence unfolded in 1848. R.I.P. Holder, Eliza and Eliza Ann Borden. Visit our Articles section above for more on this story. The coffee shop has won its suit to retain its name and has plans to expand into the shop next door and extend its menu in the near future.
More...
Lizzie Borden: Warps and Wefts - 2/12/2024
The Titanic claimed several well-known New Yorkers, some with pedigreed last names like Astor and Guggenheim. But perhaps the most famous passengers who perished after the ship met its fate in the North Atlantic on April 14, 1912 were Isidor and Ida Straus. Their devotion to each other in the last hours of their lives […]
More...
Ephemeral New York - 4/14/2025
Youth With Executioner by Nuremberg native Albrecht Dürer … although it’s dated to 1493, which was during a period of several years when Dürer worked abroad. November 13 [1617]. Burnt alive here a miller of Manberna, who however was lately … Continue reading
More...
Executed Today - 11/13/2020
National Police Gazette, December 29, 1888.Franklin Asbury Hawkins murdered his mother on October 29, 1887, and dumped her body, beaten and shot, by the side of the road in Islip, Long Island. 22-year-old Hawkins was angered that his mother objected to his desire to marry Hattie Schrecht, a servant girl. Hawkins was easily convicted of first-degree murder and sentenced to be hanged in December
More...
Murder By Gaslight - 4/12/2025
Soapy Smith STAR NotebookPage 19 - Original copy1884Courtesy of Geri Murphy(Click image to enlarge)
oapy Smith begins an empire in Denver.Operating the prize package soap sell racket in 1884.This is page 19, the continuation of page 18, and dated April 14 - May 5, 1884, the continuation of deciphering Soapy Smith's "star" notebook from the Geri Murphy's collection. A complete introduction to
More...
Soapy Smith's Soap Box - 4/3/2025
[Editor’s note: Guest writer, Peter Dickson, lives in West Sussex, England and has been working with microfilm copies of The Duncan Campbell Papers from the State Library of NSW, Sydney, Australia. The following are some of his analyses of what he has discovered from reading these papers. Dickson has contributed many transcriptions to the Jamaica […]
More...